New Material Division
New Material Division
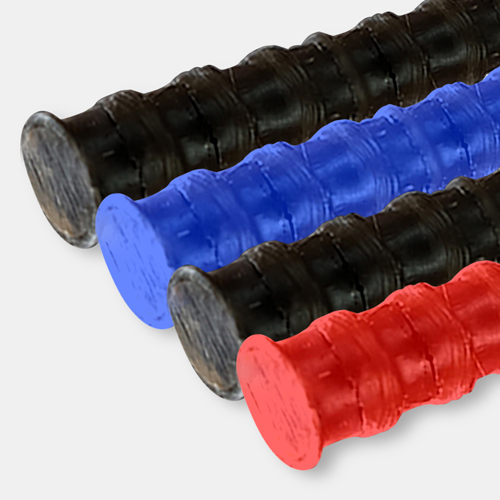

Glass (Carbon) Fiber Reinforced Polymer Rebar (GFRP/CFRP Rebar)
The next-generation construction material produced in combination of the molding and engineering technologies of the glass (carbon) fiber material with rust-resistance, high strength, and low weight, which makes it possible to expand the lifespan of buildings and structures and to improve quality and productivity.
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) Rebar Product
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) Rebar has such advantages as more strength (three times) and lower weight (1/9) than steel based rebar, corrosion resistance, low maintenance cost, and lifecycle (over 80 years) cost reduction. Therefore, with the material, it is possible to prevent deterioration of concrete structures and expand their lifespan. As a new material product, GFRP Rebar has actively been used for civil engineering, construction, bridges, tunnels, roads, railways, wind power and offshore structures, and others in advanced countries since the 2000s.
(GFRP) Rebar (comparison between GFRP Rebar and steel (Fe) Rebar)
| Metal Rebar (Fe) D13mm | GFRP Rebar D10mm |
|---|---|
| Rust and corrosion, vulnerable to salt | Excellent corrosion-resistance and chemical-resistance |
| Low tensile strength | About three times stronger tensile strength than steel rebar |
| Heavy unit weight (995g/m) | Light weight (150g/m, about 15% of the weight of steel rebar) |
| High construction cost (trailer transportation, etc.) | Construction cost saving (11t truck transportation, work efficiency improvement) |
| Possible fluctuation and rise of rebar price | More than 25% lower cost than that of rebar (flexible depending on the market price of rebar |
| Expansion and contraction as thermal conductor (heat conductivity: 46W/m℃) Causing damage by transferring fire upstairs in case of building fire | Non-conductor without thermal conductivity (heat conductivity: 0.35W/m℃) No heat transfer due to insulation, and safe |
| Vibration delivery, and vulnerable to earthquake | Shock absorption, strong for earthquake, and reduction in noise between floors |
GFRP G-Bar Production Line
G-Bar Production Line

Features and Advantages of G-Bar
- the products whose outside diameter ranges from 7mm to 32mm (discussion for special specifications)
- patented technology based on pultrusion
- High-strength and low-weight product compared to steel rebar, due to glass fiber complex material
- No corrosion, high tensile strength, and improved quality and lifespan of buildings
- Civil engineering, buildings, offshore structures, roads, railways, bridges and tunnel construction, etc.
Mechanical Properties of G-Bar
| Type | Unit | G10 | G13 | G16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex Material | Glass long fiber + Unsaturated polyester resin | |||
| Tensile Strength | MPa | 800 ~ 1,300 | ||
| Tensile Stiffness | GPa | 49 | 50 | 49 |
| Max. Load of Tension | kN | 88 | 151 | 245 |
| Flexural Strength | MPa | 912 | 791 | 645 |
| Flexural Stiffness | GPa | 41 | 44 | 29 |
| Weight | g/m | 150 | 250 | 400 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | xE-6/℃ | 6.95 | ||
| Fiber Volume Rate | % | 60.7 | ||
| Porosity | % | 0.8 | ||
| Fiber Density | g/cm³ | 2.54 | ||
| Resin Density | g/cm³ | 1.2 | ||
| Flexural Max. Load | N | 871.2 | 2481 | 4176.2 |
※ The mechanical properties are different depending on materials (glass fiber, carbon fiber, etc.) and specifications (G10, G13, G16, etc.).
New material concrete test report
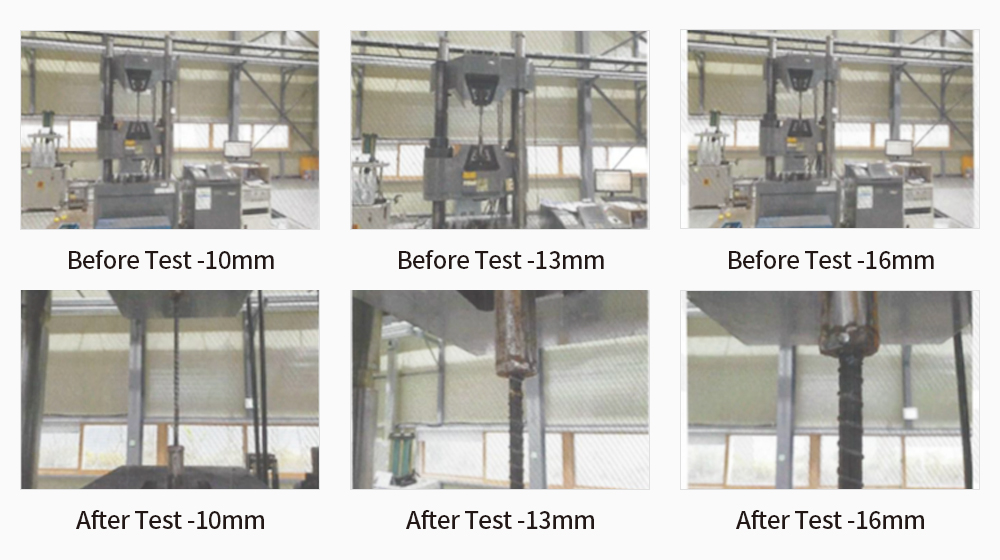
Tensile strength test (ASTM)
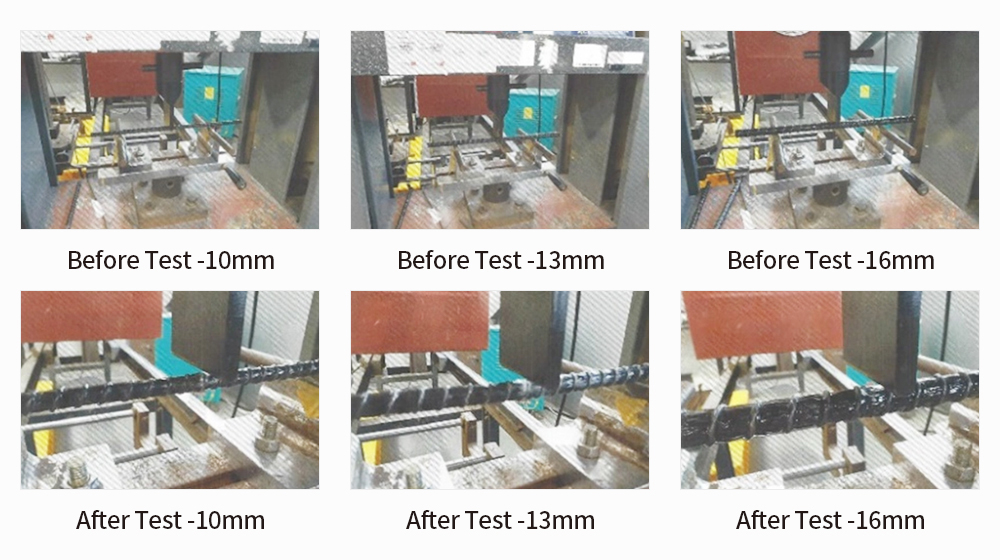
Flexural strength test (KS F 3113)

Attachment strength test (ASTM)
CFRP & GFRP Buildings and Structures Applied industrial areas

Foundation construction

Railway construction

Marine tetrapod

Onshore and offshore bridges

Offshore structures

Offshore wind power

Onshore wind power

Solar power structures





 [50875] 20-20, Techno valley 1-ro, Jillye-myeon, Gimhae-si, Gyeongsangnam-do, Republic of Korea TEL. +82-55-337-2947 FAX. +82-55-322-2947 E-MAIL. now@nowens.co.kr
[50875] 20-20, Techno valley 1-ro, Jillye-myeon, Gimhae-si, Gyeongsangnam-do, Republic of Korea TEL. +82-55-337-2947 FAX. +82-55-322-2947 E-MAIL. now@nowens.co.kr